Key Takeaways:
- Critical Severity: CVE-2026-24061 is a remote code execution (RCE) and authentication bypass vulnerability in GNU Inetutils telnetd (versions 1.9.3 through 2.7) with a CVSS score of 9.8.
- Instant Root Access: Attackers can bypass authentication entirely by injecting the value -f root into the USER environment variable during the Telnet negotiation phase.
- Significant Global Risk: Initial research indicates that approximately 800,000 devices globally are potentially exposed to this flaw.
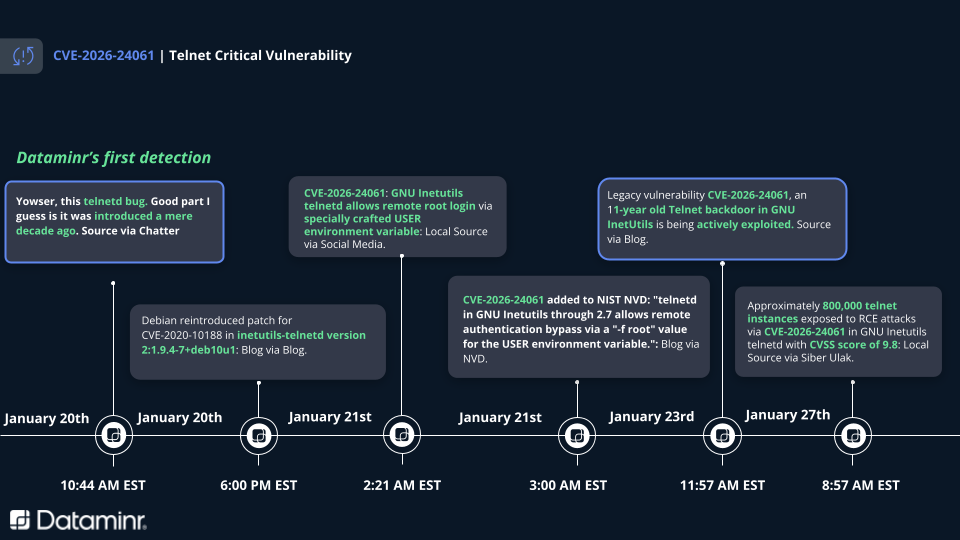
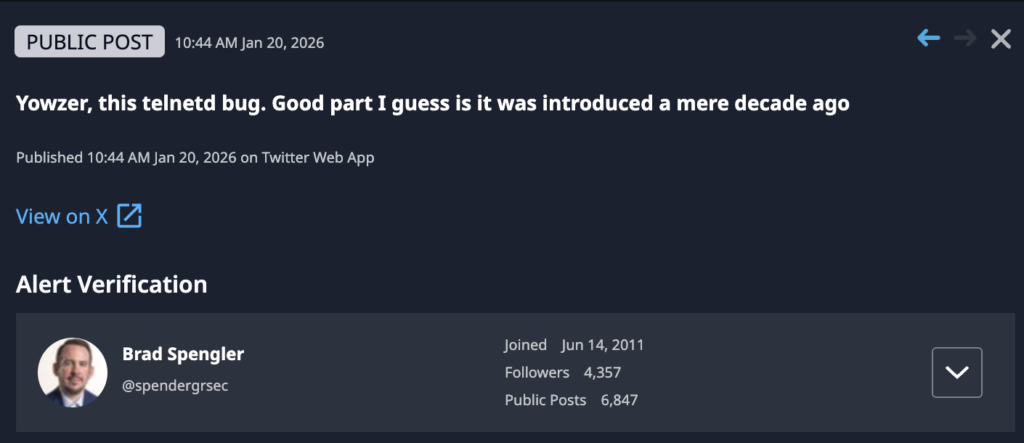
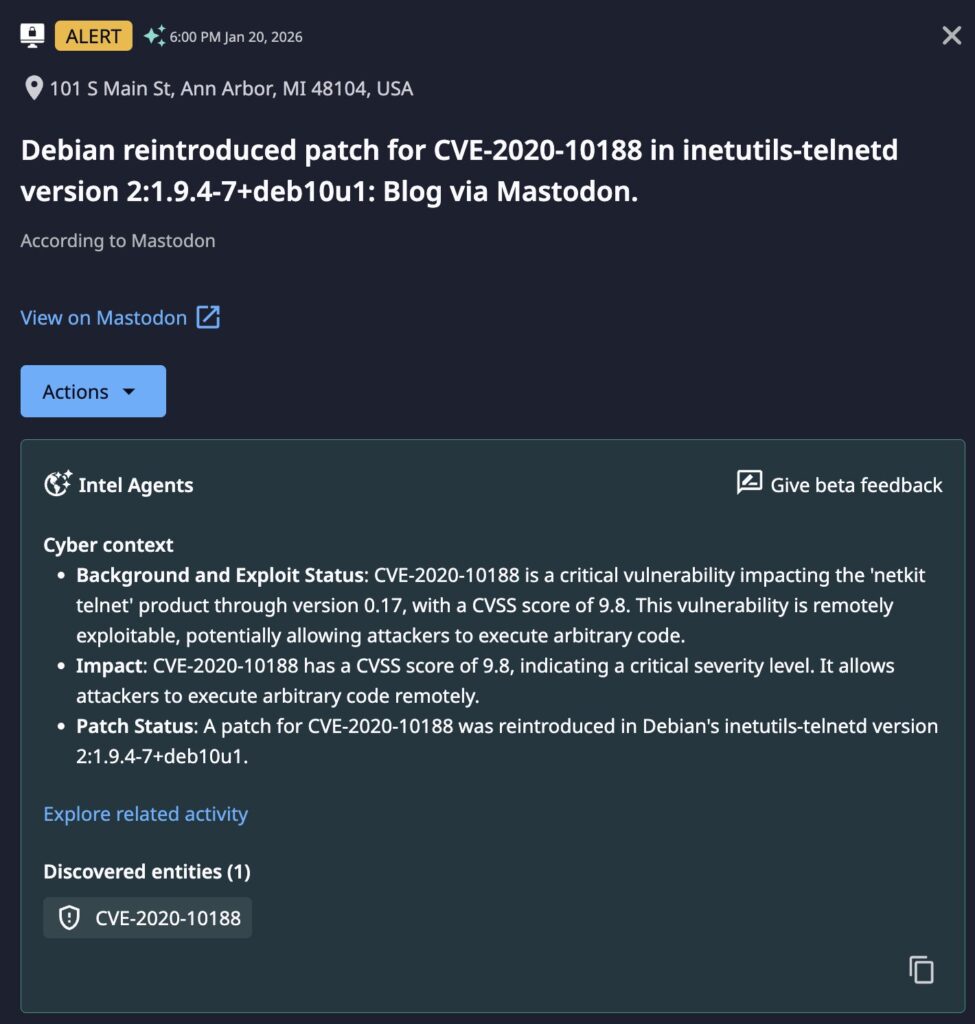
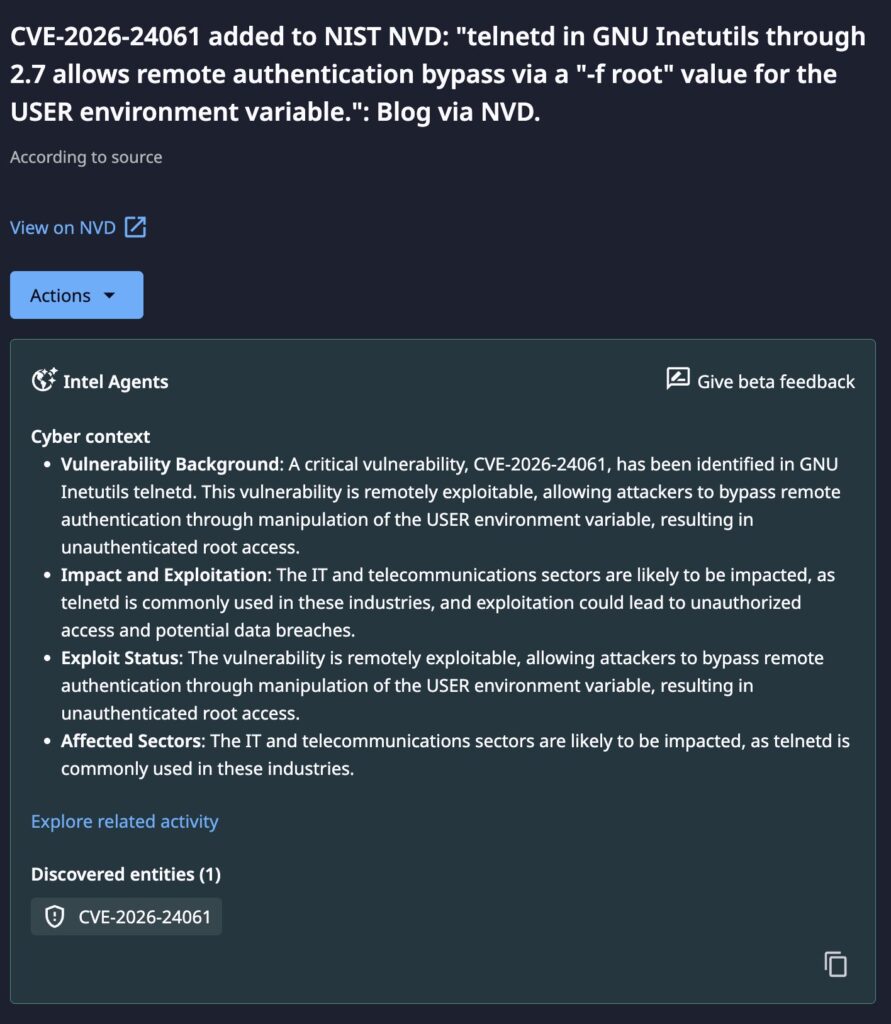
- Rapid Detection: Dataminr identified the threat following chatter early on January 20th, including a Debian patch reintroduction for CVE-2020-10188 later that day. This was roughly 24 hours before CVE-2026-24061 was formally added to the NIST NVD.
Overview of the Vulnerability
This is a critical vulnerability in the Telnet daemon (telnetd) provided by the GNU Inetutils suite. The flaw, tracked as CVE-2026-24061, enables an unauthenticated remote attacker to bypass the system’s login process and obtain an interactive root shell. This vulnerability stems from a failure to sanitize user-controlled environment variables before they are passed to the system’s login utility.
As researchers discussed the new vulnerability, an unrelated issue was noted in the original patch for CVE-2020-10188, which may have influenced an uncommon patch reintroduction. It has a CVSS score of 9.8 and allows attackers to execute arbitrary code because of a buffer overflow involving the netclear and nextitem functions.
Despite Telnet being a legacy protocol largely superseded by SSH, it remains prevalent in industrial control systems (ICS), operational technology (OT), and older Linux/Unix environments. The broad exposure of nearly a million devices highlights the persistent risk that “forgotten” or legacy services pose to modern enterprise security.
The vulnerability is classified as an Argument Injection (CWE-88) flaw. During the initial connection handshake, a Telnet client can negotiate environment variables, including USER. The vulnerable telnetd server takes this variable and expands it into the command line used to invoke the /usr/bin/login binary.
By supplying a crafted value such as -f root, an attacker forces the server to execute login -f root. On most Unix-like systems, the -f flag instructs the login utility to skip authentication for the specified user, resulting in an immediate root shell without a password prompt.
Dataminr Detection
Dataminr’s Recommendations
Threat actors are utilizing automated scanners to identify exposed Telnet services (TCP port 23) for opportunistic compromise. Successful exploitation allows for lateral movement, data exfiltration, and the installation of persistent backdoors.
To protect your organization against exploitation, Dataminr suggest taking the following actions:
- Disable the Service: The most effective mitigation is to disable telnetd entirely across the environment. Organizations should migrate all remote administration tasks to SSH, which provides encryption and robust authentication.
- Apply Security Patches: If Telnet is business-critical, immediately upgrade GNU Inetutils to version 2.8 or apply the specific patches released by your Linux distribution (e.g., Debian DSA-6106-1).
- Network Perimeter Filtering: Block all inbound traffic to TCP port 23 at the network firewall. If external access is required, it must be restricted to trusted IP ranges via a VPN.
- Threat Hunting: Review system logs for login processes invoked with the -f flag and audit for unauthorized root logins that lack a corresponding authentication event in security logs.

Get Ahead of Emerging Threat Activity
Proactively adjust your cybersecurity posture based on comprehensive AI-powered real-time threat intelligence.
Learn More



