Key Takeaways
- CVE-2025-9491 is a zero-day vulnerability found in Fortinet’s web application firewall (WAF) solution FortiWeb.
- Successfully exploiting this vulnerability could grant attackers admin-level privileges to applications that are behind vulnerable versions of FortiWeb.
- Dataminr first alerted customers about the original post concerning this vulnerability by Defused back on October 7, then again on November 13 when Watchtowr released their full report.
Overview of the Vulnerability
Watchtowr Labs recently published an in-depth analysis based on Defused Cyber’s discovery of a zero-day exploit affecting Fortinet’s FortiWeb solution. Successfully exploiting this vulnerability could allow an attacker access to files and functionality within web applications and APIs that FortiWeb is supposed to be protecting.
CVE-2025-64446 was originally tagged by Defused as a potential variant of an older authentication bypass vulnerability identified in 2022 that also affected Fortinet devices. However, upon continued research it was discovered that this was a novel vulnerability and required its own set of fixes. Additional analysis by researchers indicate exploitation of this vulnerability may go back years, although such claims are unconfirmed at this time. Following public disclosure, Fortinet released a security update and a CVE number was assigned, although review of patches indicate this may have been silently fixed in an earlier release for FortiWeb 8.02.
FortiWeb is a web application firewall (WAF) used to protect web applications and APIs from attacks. For CVE-2025-64446, an adversary can identify an accessible, vulnerable FortiWeb instance and send a specially crafted HTTP or HTTPS request allowing for arbitrary command execution at privileged levels on the device. Examples of such activity include adding administrator-level accounts to the device that can then be abused for follow-on activity on the vulnerable FortiWeb instance.
Dataminr’s Detection
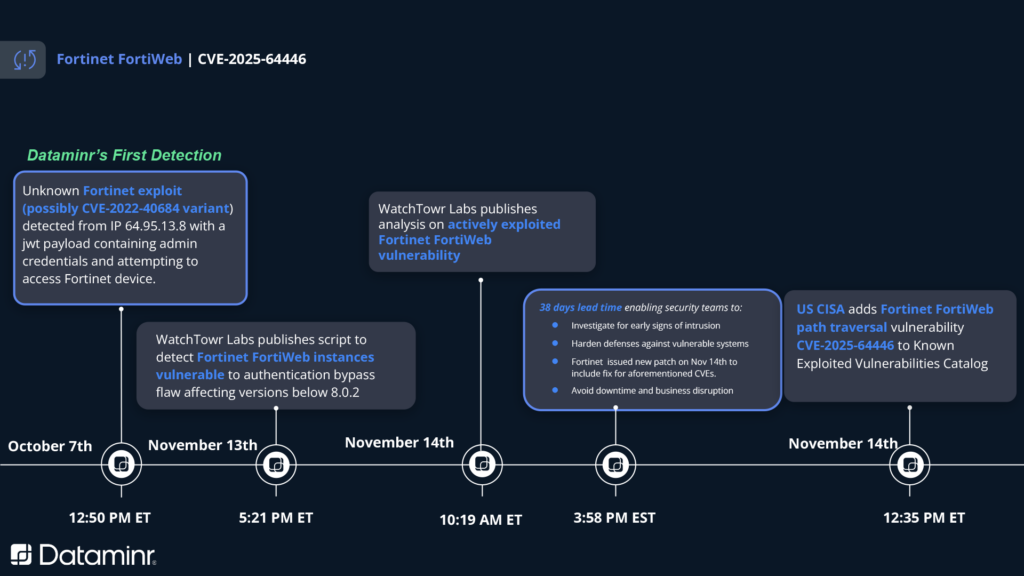

Dataminr’s Recommendations
Vulnerabilities such as CVE-2025-64446 are especially concerning given their ability to impact external-facing assets with a high degree of severity. Patching is an obvious action to eliminate such vulnerabilities, but in this particular example the vulnerability in question was exploited for at least a month (and possibly quite longer) prior to patch release. In these instances, organizations must adopt a combination of best defensive practices and defense in depth.
Reduce attack surface
Even for external-facing assets such as firewalls or similar, critical resources such as administrative portals should rarely (if ever) be exposed to the internet. If external remote access is necessary, use of VPNs or similar solutions can reduce attack surface and avoid direct exposure of sensitive resources for exploitation or brute force logon.
Monitor for anomalous activity across internal and external assets
This is not just desirable but increasingly necessary. Auditing items such as new user creation, external logon activity, and similar is now a minimal requirement for enterprise security given the popularity of exploitation or credential replay actions against such assets. Unfortunately, many organizations either do not or cannot monitor for such activity as the relevant logs are difficult to come by, not ingested into common streams for presentation in the SIEM, or related reasons. As a result organizations must work to centralize and expand visibility to identify the actions associated with true zero day exploitation such as in CVE-2025-64446.
Identify risk as early as possible
Finally, organizations must maintain situational awareness of the overall threat landscape. Initial reporting on this activity emerged in early October 2025—a month in advance of official notification. Identifying such items of concern as early as possible can allow organizations to implement compensating controls and initiate threat hunts and similar more rapidly in response to events.

Dataminr Pulse for Cyber Risk
Learn more about how Dataminr helps cybersecurity customers evaluate and prioritize vulnerabilities.
Learn More



