Key takeaways
- Critical Severity: CVE-2025-59718 (CVSS 9.8) allows unauthenticated remote attackers to bypass FortiCloud SSO login authentication on multiple Fortinet products. CVE-2025-59719 (CVSS 9.8) also allows for FortiCloud SSO login bypass in specific FortiWeb versions.
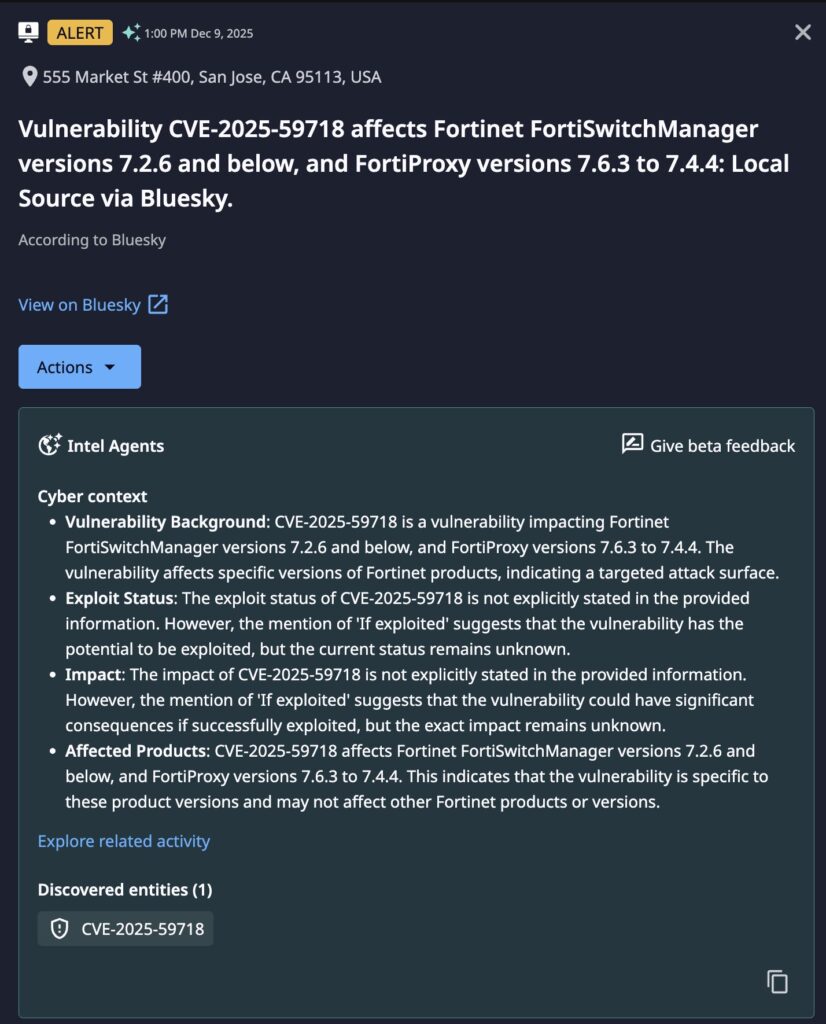
- Early Detection: Dataminr first detected disclosure of these vulnerabilities on December 9th, 2025.
- Active Exploitation: Threat actors have been actively exploiting these vulnerabilities since at least December 13, 2025, targeting Fortinet honeypots and executing malicious SSO logins on FortiGate appliances.
- Widespread Risk: Network scan data indicates there are 30,044 internet-exposed instances with FortiCloud SSO enabled that are potentially vulnerable. The potential financial impact of these two CVEs going unpatched could range from roughly $200k to more than $7M.
- Immediate Action: CISA has mandated remediation; organizations should apply official patches immediately or disable FortiCloud SSO as a workaround.
- Compensating Controls: Ensure controls that mitigate the techniques used to exploit these CVEs are enabled. These include enabling Executable File Scanning and implementing application isolation, sandboxing, or micro-segmentation for authentication-related services.
Overview of the vulnerability
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has added two critical vulnerabilities to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog: CVE-2025-59718 and CVE-2025-59719.
CVE-2025-59718 is a critical “Improper Verification of Cryptographic Signature” vulnerability with a CVSS score of 9.8. It impacts multiple products, including FortiOS, FortiProxy, FortiSwitchManager, and FortiWeb. Successful exploitation allows a remote, unauthenticated attacker to bypass the FortiCloud Single Sign-On (SSO) login process, granting unauthorized access to the device management interface.
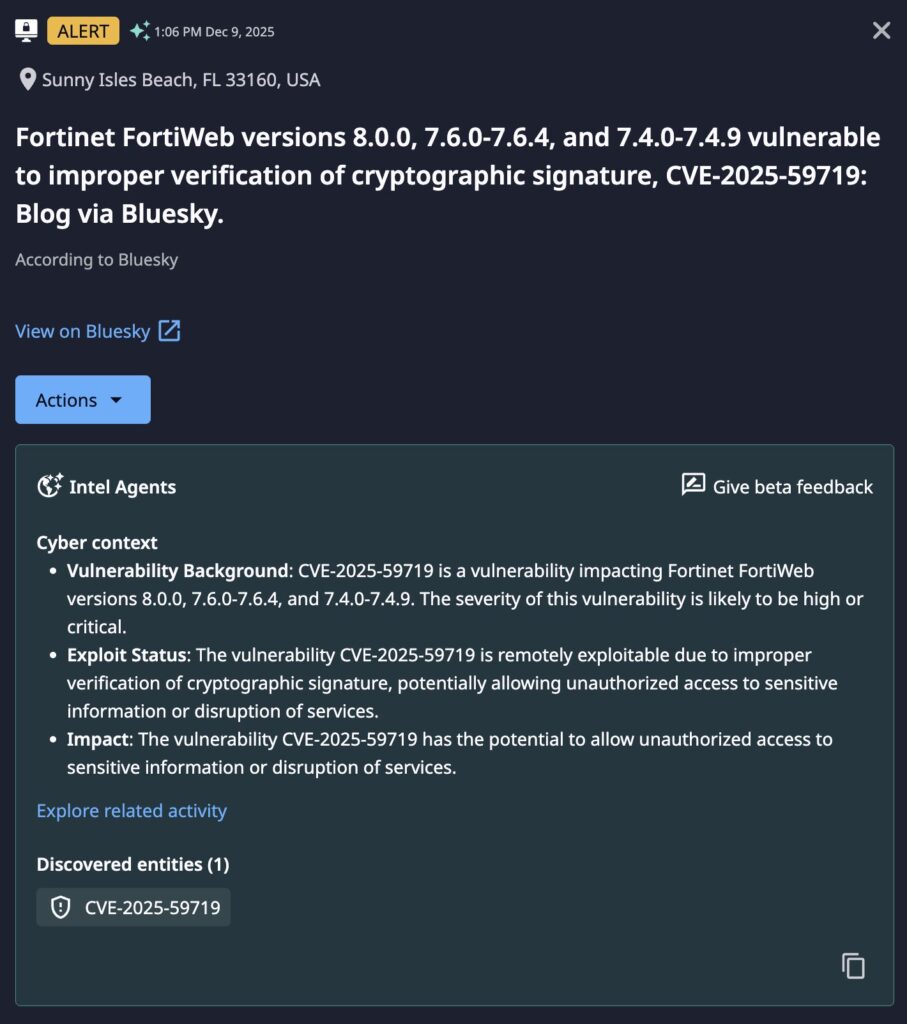
CVE-2025-59719, also carrying a CVSS score of 9.8, is also a bypass mechanism for FortiCloud SSO that specifically impacts FortiWeb versions 8.0.0, 7.6.0 through 7.6.4, and 7.4.0 through 7.4.9. Security researchers at VulnCheck and Arctic Wolf have confirmed active exploitation in the wild, observing attacker infrastructure targeting Fortinet honeypots and malicious SSO logins on production FortiGate appliances.
Current network telemetry reports 189,212 internet-exposed FortiOS 7.x admin GUIs, with approximately 30,044 of those instances having FortiCloud SSO enabled and potentially exposed to this specific bypass vector.
Dataminr’s Detection
Based on analysis from ThreatConnect Risk Quantifier (RQ), powered by Dataminr, which examines the risk profile of companies ranging from $1B to $10B across multiple industries, the projected financial impact of exploitation ranges from approximately $200K to potentially more than $7M. Impact scenarios depend on industry, organizational scale, and the maturity of the defensive stack and compensating controls.
Threat detection timeline:

Dataminr’s Recommendations
Patch Immediately: Apply the official security updates provided by Fortinet for FortiOS, FortiProxy, FortiWeb, and FortiSwitchManager immediately, as per CISA mandates.
Disable SSO (Workaround): If immediate patching is not feasible, Fortinet recommends disabling the Single Sign-On (SSO) feature for the FortiCloud authentication system to mitigate the bypass vector.
Review Access Logs: Security teams should audit logs for unusual authentication activity or unexpected administrative sessions initiated via FortiCloud, particularly on FortiGate appliances.
Restrict Management Interfaces: Ensure administrative interfaces are not directly exposed to the public internet whenever possible. Use VPNs or similar mechanisms to limit access to management portals to minimize attack surface.

Preempt Breaches with Actionable Vulnerability Intelligence
Learn more about how Dataminr helps cybersecurity customers evaluate and prioritize vulnerabilities.
Learn More



