In today’s hyper-connected world, cyber threats evolve faster than ever, making it critical for organizations to stay one step ahead. Traditional cybersecurity measures, which rely on manual monitoring and static defense mechanisms, are often too slow to catch increasingly sophisticated attacks.
This is where artificial intelligence (AI) comes into play. With the ability to analyze vast amounts of data and recognize patterns at unprecedented speed, AI is revolutionizing real-time threat detection and providing organizations with the tools they need to proactively defend against cyber threats.
In fact, real-time threat detection is one of the most powerful applications of AI in cybersecurity, according to the AFCEA International Cyber Committee white paper, “Navigating the Future of Cybersecurity with Artificial Intelligence.”
Let’s dive deeper into how AI is reshaping this critical area.
The role of AI in threat detection
In cybersecurity, time is everything. The faster a threat is detected, the quicker it can be neutralized, preventing further damage. However, many attacks—like zero-day vulnerabilities, ransomware, or data leaks—move too quickly for traditional systems to catch up.
The role AI models play in real-time threat detection include:
- Identifying and collecting relevant signals
- Correlating those signals to comprehend relevant events, and characterizing them as the types of events they are
- Extracting relevant metadata to deliver tailored reporting, continually updating as the situation develops
AI has the ability to help organizations detect new and evolving cyber threats in public data through:
- Speed. Proactively manage cyber risks in real time and acting at the first opportunity
- Scope. Continuously monitor across an exceptionally broad threat landscape to avoid missed threats
- Relevance. Cut through the noise by prioritizing and managing risk through relevant and actionable alerts
Continuous monitoring of internal system data is not enough
Many organizations are looking to redefine their cyber risk management strategies to become more proactive and resilient. They have already invested heavily in building robust programs and platforms to correlate their internal data within their enterprise—along with manual methods of identifying and responding to these threats that can leave organizations vulnerable for hours, days, or even weeks.
Even when leveraging AI and automation technologies for continuous monitoring strategies, organizations are working in a reactive mode on events that have already occurred in their environment.
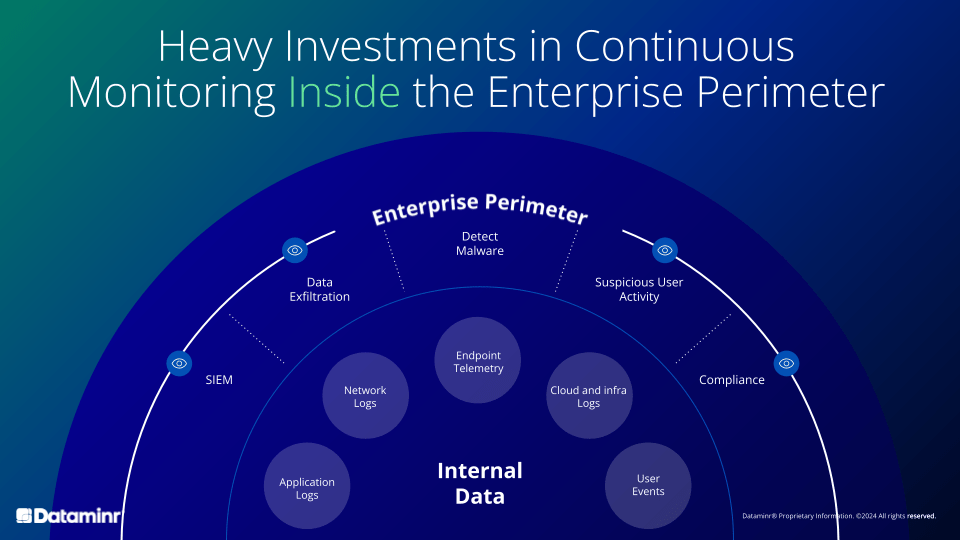
This approach still leaves many blind spots. Just as a team is only as strong as its weakest link, so too is an organization’s cyber risk from its third parties, particularly organizations and technologies that process, store or have access to sensitive data or are part of mission critical systems.
Within the public sector this is even more of a challenge as an organization’s supply chain is much more visible because of financial transparency regulations and sites like the U.S. government website usaspending.gov. The U.S. government is not alone here. Many state and municipal government organizations also have Open Checkbook programs and sites like openthebooks.com aggregate these sites into a central repository.
Third-party Vulnerabilities Put the Public Sector at Risk: What to Consider
A look at why and which questions public sector organizations should ask to help strengthen their controls and gain greater visibility into potential threats.
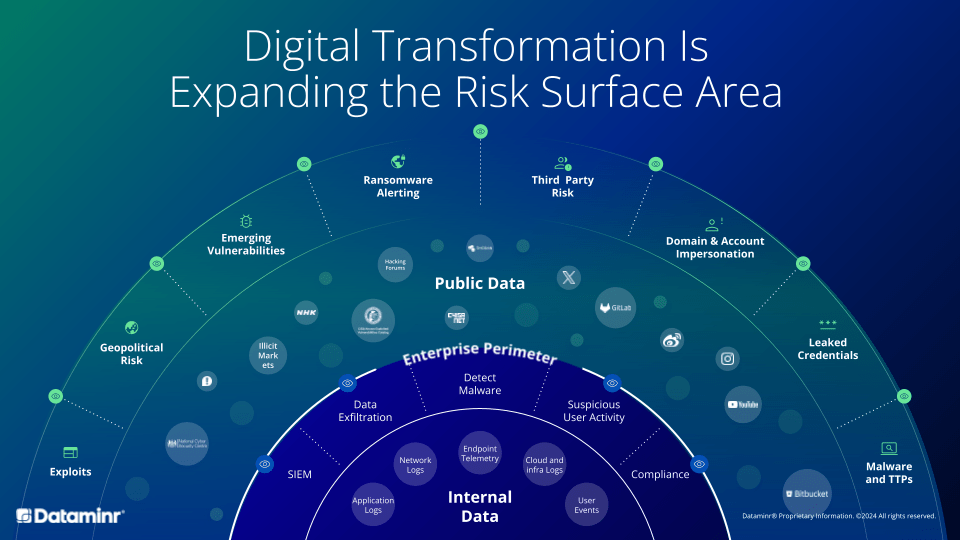
Learn MoreIf public sector organizations are looking to take a more proactive approach to detecting threats early in the kill chain—or prevent threats before they occur—they must look to apply the same continuous monitoring concepts to detect these indicators in real time outside of their organization’s networks.
While these indicators of risk exist in publicly available domains, they can be very challenging to detect because:
- The sheer volume of data to be able to process in massive, larger than any one organization’s own internal data
- Information can be obfuscated from many disparate sources that are constantly being created, changing and moving
- The cyber threat landscape is global with threat actors that are constantly shifting, splintering and evolving along with their tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs) and malware toolkits
The concept of an external SIEM
AI platforms such as Dataminr’s leverage AI to ingest massive amounts of data across various sources, both structured and unstructured. These sources can range:
- Traditional social media like X or regional or alternative social media such as message boards
- Code repositories, like Gitlab or Bitbucket
- Public sensors such as IoT and IP scanning
- The deep and dark web, including illicit forums and dump sites
- Industry blogs and publications
- Government and corporate advisories
- Traditional news media
Dataminr currently ingests data from over 1.1 million different public data sources and processes over 43 terabytes of text, image, video and sensor data a day.
Real-world examples of AI in real-time detection
- October 2024: When Dataminr’s customer, a government-run city airport, was alerted to a DDos attack against another nearby airport, it immediately reinforced its systems. Eight minutes later, the airport was hit with a DDoS attack that lasted 11 minutes with over 3 million hits but with no success. Because it was alerted to the threat in real time, the airport had the lead time needed to ensure it was ready for an attack.
- September 2023: A U.S. federal agency was able to detect sale of network access to a management consulting firm that has access to sensitive organizational data and notify it immediately, ensuring the clients systems and the agency’s data was not compromised.
Watch Video: Amtrak CISO on AI for External Threat Detection
The rapidly evolving cyber threat landscape demands that organizations move beyond traditional, reactive approaches to security. AI-driven real-time threat detection is not just a technological advancement—it’s a necessity. By harnessing the power of AI to process vast datasets, identify subtle patterns, and deliver actionable insights at unprecedented speed, organizations can shift from a reactive posture to a proactive defense strategy.
From preventing DDoS attacks to safeguarding sensitive networks, real-world applications of AI in real-time threat detection underscore its transformative potential. As cyber risks grow more sophisticated, the ability to detect and act on threats in real time will define the future of resilient and effective cybersecurity.
The challenge is clear: staying ahead of cyber adversaries requires embracing innovation and leveraging the power of AI to protect what matters most. The time to act is now.

Dataminr Pulse for Cyber Risk: Public Sector Demo
Get a first-hand look at how public sector organizations use Dataminr Pulse for Cyber Risk for real-time cyber threat detection, including digital risk, vulnerability intelligence and third-party risk.
Watch Now